We live in the age of AI, where imagination is becoming a reality. Artificial intelligence, which was a story in science fiction, is now being used in various parts of everyday life in ways we could not have imagined.
New devices powered by artificial intelligence are changing the way humans interact with and utilize technology, making our lives smarter.
Find out what artificial intelligence is and how it is changing lives with Samsung Semiconductor.
We live in the age of AI, where imagination is becoming a reality. Artificial intelligence, which was a story in science fiction, is now being used in various parts of everyday life in ways we could not have imagined.
New devices powered by artificial intelligence are changing the way humans interact with and utilize technology, making our lives smarter.
Find out what artificial intelligence is and how it is changing lives with Samsung Semiconductor.
We live in the age of AI, where imagination is becoming a reality. Artificial intelligence, which was a story in science fiction, is now being used in various parts of everyday life in ways we could not have imagined.
New devices powered by artificial intelligence are changing the way humans interact with and utilize technology, making our lives smarter.
Find out what artificial intelligence is and how it is changing lives with Samsung Semiconductor.
Artificial intelligence, also known as AI, is a branch of computer science that studies how to apply intelligent human-like behavior to mechanical systems. In other words, artificial intelligence makes mechanical systems like computers and robots think like humans do.
When artificial intelligence is given a task, it selects an appropriate answer by collecting and analyzing information from its surrounding environment, and if it makes a mistake, it learns alternatives so it can do better next time. Artificial intelligence is an umbrella term for a wide range of technologies, including machine learning and natural language processing.
Today, it is used in a variety of industries, from smartphones and home appliances to autonomous driving cars, industrial manufacturing, and healthcare. This is only the beginning. Artificial intelligence will soon exist everywhere in our lives.
Artificial intelligence, also known as AI, is a branch of computer science that studies how to apply intelligent human-like behavior to mechanical systems. In other words, artificial intelligence makes mechanical systems like computers and robots think like humans do.
When artificial intelligence is given a task, it selects an appropriate answer by collecting and analyzing information from its surrounding environment, and if it makes a mistake, it learns alternatives so it can do better next time. Artificial intelligence is an umbrella term for a wide range of technologies, including machine learning and natural language processing.
Today, it is used in a variety of industries, from smartphones and home appliances to autonomous driving cars, industrial manufacturing, and healthcare. This is only the beginning. Artificial intelligence will soon exist everywhere in our lives.
Artificial intelligence, also known as AI, is a branch of computer science that studies how to apply intelligent human-like behavior to mechanical systems. In other words, artificial intelligence makes mechanical systems like computers and robots think like humans do.
When artificial intelligence is given a task, it selects an appropriate answer by collecting and analyzing information from its surrounding environment, and if it makes a mistake, it learns alternatives so it can do better next time. Artificial intelligence is an umbrella term for a wide range of technologies, including machine learning and natural language processing.
Today, it is used in a variety of industries, from smartphones and home appliances to autonomous driving cars, industrial manufacturing, and healthcare. This is only the beginning. Artificial intelligence will soon exist everywhere in our lives.

Perhaps the simplest way to think of AI is as technology that enables devices to perform tasks that require human-like cognition. Image and speech recognition are clear markers of such intelligence, and two areas where AI is rapidly advancing.
Image recognition systems are quickly becoming capable of not just recognizing objects and facial expressions, but also the context and nuance behind them. Some can even utilize this insight to generate completely new, ultra-realistic images.
Speech recognition systems are leveraging deep learning to analyze billions of words, along with complex phrases and sentence structures, and enable intelligent assistant services to understand and respond to users’ sophisticated commands.
Perhaps the simplest way to think of AI is as technology that enables devices to perform tasks that require human-like cognition. Image and speech recognition are clear markers of such intelligence, and two areas where AI is rapidly advancing.
Image recognition systems are quickly becoming capable of not just recognizing objects and facial expressions, but also the context and nuance behind them. Some can even utilize this insight to generate completely new, ultra-realistic images.
Speech recognition systems are leveraging deep learning to analyze billions of words, along with complex phrases and sentence structures, and enable intelligent assistant services to understand and respond to users’ sophisticated commands.
Perhaps the simplest way to think of AI is as technology that enables devices to perform tasks that require human-like cognition. Image and speech recognition are clear markers of such intelligence, and two areas where AI is rapidly advancing.
Image recognition systems are quickly becoming capable of not just recognizing objects and facial expressions, but also the context and nuance behind them. Some can even utilize this insight to generate completely new, ultra-realistic images.
Speech recognition systems are leveraging deep learning to analyze billions of words, along with complex phrases and sentence structures, and enable intelligent assistant services to understand and respond to users’ sophisticated commands.
For devices to think for themselves, machine learning is necessary.
Machine learning is a sub-concept of AI that focuses on building applications that can learn from data to improve accuracy over time. Instead of programming computer to perform a specific task, it is taught to identify patterns in data and make confident decisions on its own.
Deep learning is a sub-concept of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks, algorithms found in the structure of the human brain, to identify patterns in large amounts of data. Deep learning is key element in image classification and natural language analysis, and has advanced to a level that surpasses humans, and is being applied to applications such as autonomous driving as well as translation.
For devices to think for themselves, machine learning is necessary.
Machine learning is a sub-concept of AI that focuses on building applications that can learn from data to improve accuracy over time. Instead of programming computer to perform a specific task, it is taught to identify patterns in data and make confident decisions on its own.
Deep learning is a sub-concept of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks, algorithms found in the structure of the human brain, to identify patterns in large amounts of data. Deep learning is key element in image classification and natural language analysis, and has advanced to a level that surpasses humans, and is being applied to applications such as autonomous driving as well as translation.
For devices to think for themselves, machine learning is necessary.
Machine learning is a sub-concept of AI that focuses on building applications that can learn from data to improve accuracy over time. Instead of programming computer to perform a specific task, it is taught to identify patterns in data and make confident decisions on its own.
Deep learning is a sub-concept of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks, algorithms found in the structure of the human brain, to identify patterns in large amounts of data. Deep learning is key element in image classification and natural language analysis, and has advanced to a level that surpasses humans, and is being applied to applications such as autonomous driving as well as translation.

Artificial intelligence has the ability to reason and draw new judgments or conclusions based on existing data and results.
Based on deep learning, AI can think more flexibly like humans and also judge the relative relationship between recognized objects. These capabilities of AI will provide new experiences in various areas of our lives, from simple work to artistic creation.
Super-giant artificial intelligence, which has recently become a hot topic, is also evolving through this reasoning ability. Unlike early AI models that needed programmed commands to output results, Generative AI models can generate results by reasoning about given situations and commands based on learning from large amounts of data.
Artificial intelligence has the ability to reason and draw new judgments or conclusions based on existing data and results.
Based on deep learning, AI can think more flexibly like humans and also judge the relative relationship between recognized objects. These capabilities of AI will provide new experiences in various areas of our lives, from simple work to artistic creation.
Super-giant artificial intelligence, which has recently become a hot topic, is also evolving through this reasoning ability. Unlike early AI models that needed programmed commands to output results, Generative AI models can generate results by reasoning about given situations and commands based on learning from large amounts of data.
Artificial intelligence has the ability to reason and draw new judgments or conclusions based on existing data and results.
Based on deep learning, AI can think more flexibly like humans and also judge the relative relationship between recognized objects. These capabilities of AI will provide new experiences in various areas of our lives, from simple work to artistic creation.
Super-giant artificial intelligence, which has recently become a hot topic, is also evolving through this reasoning ability. Unlike early AI models that needed programmed commands to output results, Generative AI models can generate results by reasoning about given situations and commands based on learning from large amounts of data.

When people make decisions, they consider immediate as well as future impacts. Sometimes, even if it doesn't bring the best results right away, they will make choices that will pay off more in the long run.
Many super-giant AI systems today are being trained to make such decisions. The AI systems even “imagine” the consequences of each option to see the problem from a larger perspective and find the highest probability of achieving their final goal.
When people make decisions, they consider immediate as well as future impacts. Sometimes, even if it doesn't bring the best results right away, they will make choices that will pay off more in the long run.
Many super-giant AI systems today are being trained to make such decisions. The AI systems even “imagine” the consequences of each option to see the problem from a larger perspective and find the highest probability of achieving their final goal.
When people make decisions, they consider immediate as well as future impacts. Sometimes, even if it doesn't bring the best results right away, they will make choices that will pay off more in the long run.
Many super-giant AI systems today are being trained to make such decisions. The AI systems even “imagine” the consequences of each option to see the problem from a larger perspective and find the highest probability of achieving their final goal.

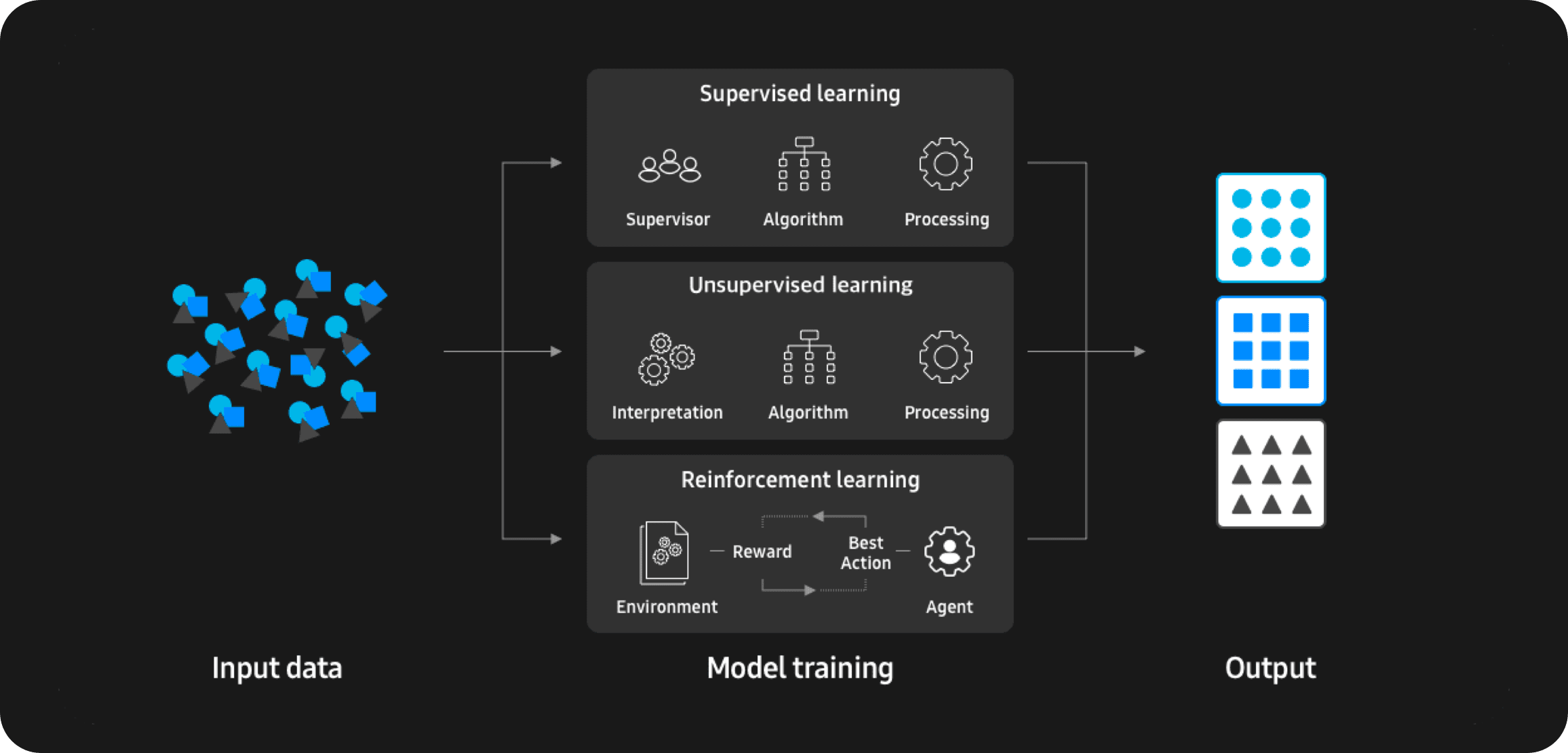
Machine learning is the process which enables AI to analyze complex data and anticipate future actions automatically. By categorizing data with labels through supervised learning and identifying patterns in data sets via unsupervised learning, the process gives machines the ability to help us make decisions quicker and with greater accuracy.
With reinforcement learning methods, a process which resembles how people and animals learn through trial and error, machines and devices can expand their capabilities independently without explicit programming. Together, these processes form the foundation for all AI-enabled features and functionalities.
Machine learning is the process which enables AI to analyze complex data and anticipate future actions automatically. By categorizing data with labels through supervised learning and identifying patterns in data sets via unsupervised learning, the process gives machines the ability to help us make decisions quicker and with greater accuracy.
With reinforcement learning methods, a process which resembles how people and animals learn through trial and error, machines and devices can expand their capabilities independently without explicit programming. Together, these processes form the foundation for all AI-enabled features and functionalities.
Machine learning is the process which enables AI to analyze complex data and anticipate future actions automatically. By categorizing data with labels through supervised learning and identifying patterns in data sets via unsupervised learning, the process gives machines the ability to help us make decisions quicker and with greater accuracy.
With reinforcement learning methods, a process which resembles how people and animals learn through trial and error, machines and devices can expand their capabilities independently without explicit programming. Together, these processes form the foundation for all AI-enabled features and functionalities.
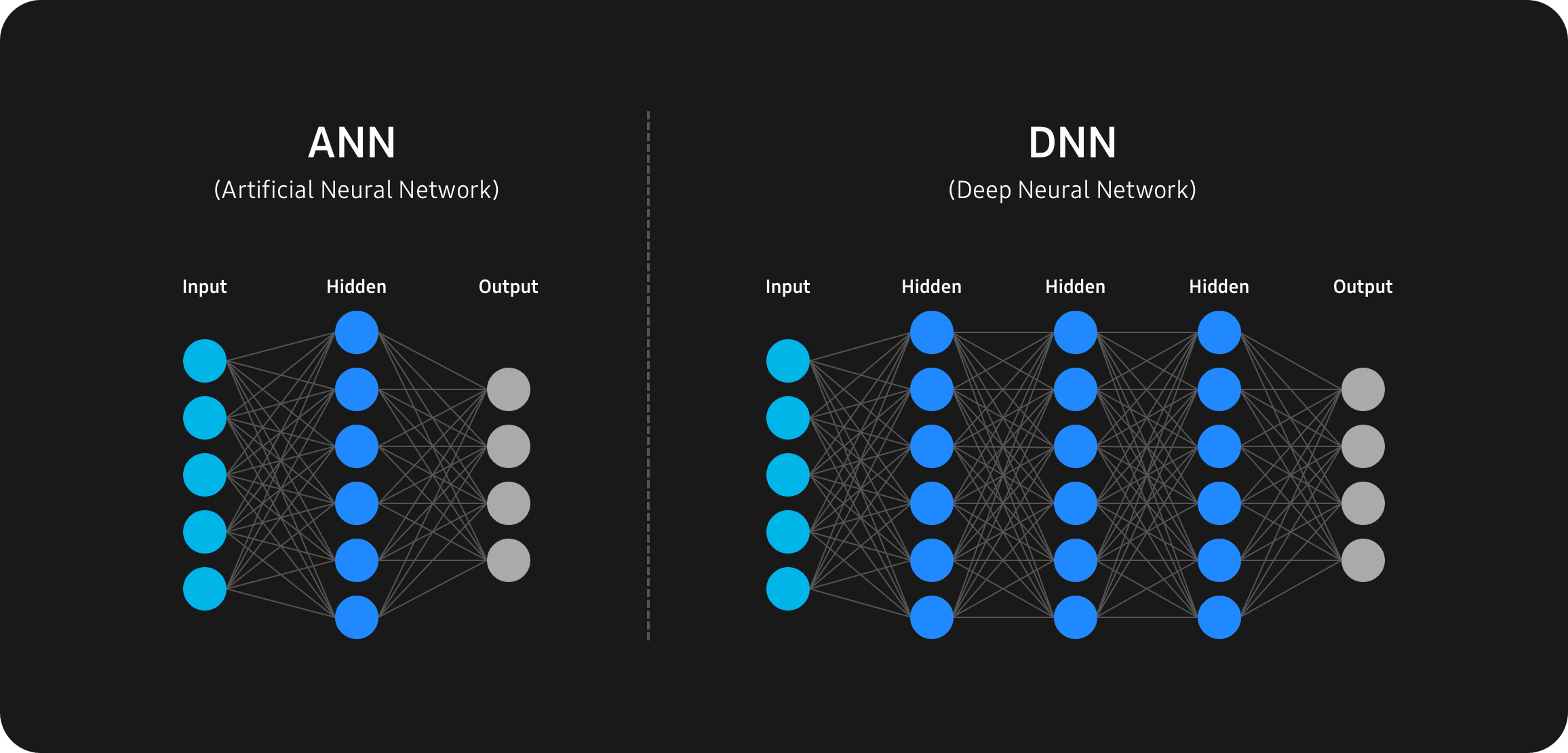
Thanks to deep learning, the devices can now analyze and recognize input data such as images and objects with incredible accuracy.
This capability is enabled by artificial neural networks (ANNs) composed of interconnected layers of algorithms, known as neurons, that are capable of processing and learning from data in a similar way to us.
Deep Neural Network (DNN) is an artificial neural network that contains multiple layers between the input and output. Similar to the way a human brain functions, DNN operates by passing the input through the layers of connected neurons for processing.
Convolution, a linear mathematical operation, is typically employed to identify patterns in data for image, speech, and natural language processing.
Thanks to deep learning, the devices can now analyze and recognize input data such as images and objects with incredible accuracy.
This capability is enabled by artificial neural networks (ANNs) composed of interconnected layers of algorithms, known as neurons, that are capable of processing and learning from data in a similar way to us.
Deep Neural Network (DNN) is an artificial neural network that contains multiple layers between the input and output. Similar to the way a human brain functions, DNN operates by passing the input through the layers of connected neurons for processing.
Convolution, a linear mathematical operation, is typically employed to identify patterns in data for image, speech, and natural language processing.
Thanks to deep learning, the devices can now analyze and recognize input data such as images and objects with incredible accuracy.
This capability is enabled by artificial neural networks (ANNs) composed of interconnected layers of algorithms, known as neurons, that are capable of processing and learning from data in a similar way to us.
Deep Neural Network (DNN) is an artificial neural network that contains multiple layers between the input and output. Similar to the way a human brain functions, DNN operates by passing the input through the layers of connected neurons for processing.
Convolution, a linear mathematical operation, is typically employed to identify patterns in data for image, speech, and natural language processing.
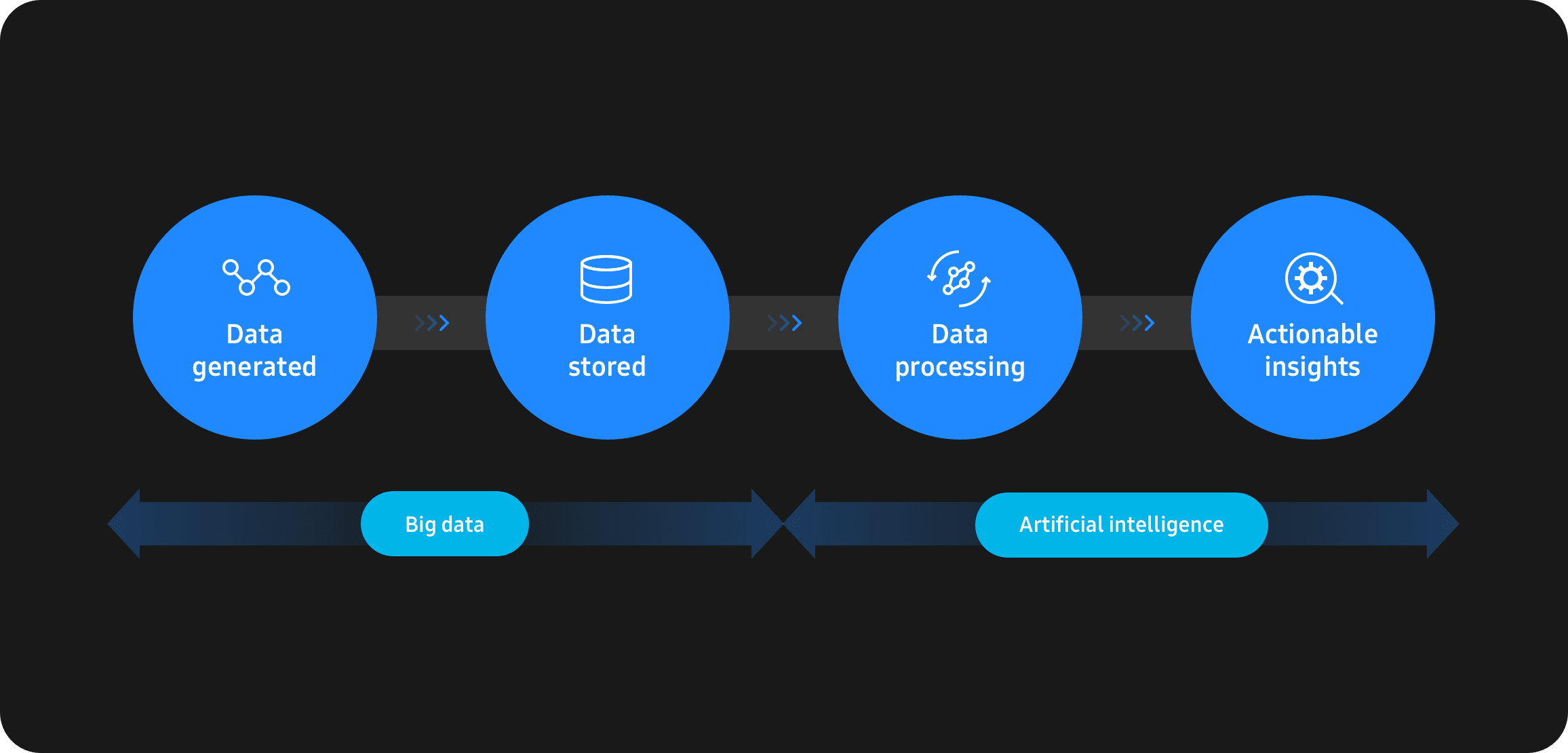
One of the most exciting applications for AI involves the processing of Big Data – or data sets so large and complex that they cannot be processed using traditional techniques. Businesses prioritize Big Data because, if analyzed properly, such data sets might reveal valuable insights that could aid them in decision making.
With AI, analysts will be able to feed massive amounts of data into a machine-learning algorithm that’s capable of sifting through and analyzing the information much faster and more efficiently than a human ever could – making it easier for enterprises to capitalize on any insights that the data may hold.
One of the most exciting applications for AI involves the processing of Big Data – or data sets so large and complex that they cannot be processed using traditional techniques. Businesses prioritize Big Data because, if analyzed properly, such data sets might reveal valuable insights that could aid them in decision making.
With AI, analysts will be able to feed massive amounts of data into a machine-learning algorithm that’s capable of sifting through and analyzing the information much faster and more efficiently than a human ever could – making it easier for enterprises to capitalize on any insights that the data may hold.
One of the most exciting applications for AI involves the processing of Big Data – or data sets so large and complex that they cannot be processed using traditional techniques. Businesses prioritize Big Data because, if analyzed properly, such data sets might reveal valuable insights that could aid them in decision making.
With AI, analysts will be able to feed massive amounts of data into a machine-learning algorithm that’s capable of sifting through and analyzing the information much faster and more efficiently than a human ever could – making it easier for enterprises to capitalize on any insights that the data may hold.
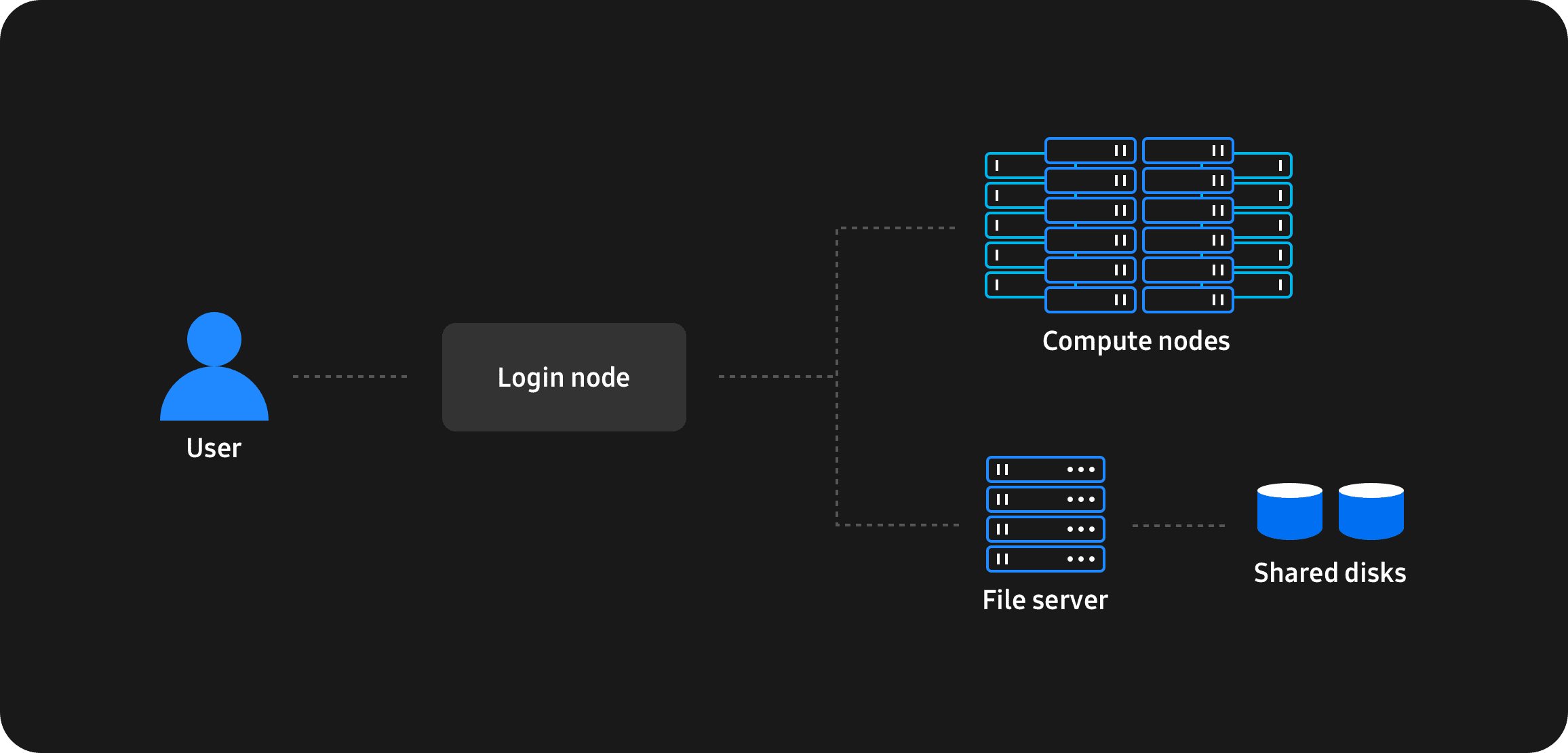
Taking AI to the next level will require advancements in high-performance computing (HPC). HPC, which describes the ability to process data and carry out complex calculations at speeds that most computers and servers simply cannot match, is currently being used to manage vast amounts of data for a variety of uses, including high-performance data analytics and the training of machine learning models.
By enabling parallel processing, in which compute servers – known as nodes – work together to boost processing power, HPC allows systems to run advanced, large-scale applications quickly and reliably. Such efficiency adds up to dramatic increases in throughput, which is necessary for processing the exponential amounts of data that come with AI.
Taking AI to the next level will require advancements in high-performance computing (HPC). HPC, which describes the ability to process data and carry out complex calculations at speeds that most computers and servers simply cannot match, is currently being used to manage vast amounts of data for a variety of uses, including high-performance data analytics and the training of machine learning models.
By enabling parallel processing, in which compute servers – known as nodes – work together to boost processing power, HPC allows systems to run advanced, large-scale applications quickly and reliably. Such efficiency adds up to dramatic increases in throughput, which is necessary for processing the exponential amounts of data that come with AI.
Taking AI to the next level will require advancements in high-performance computing (HPC). HPC, which describes the ability to process data and carry out complex calculations at speeds that most computers and servers simply cannot match, is currently being used to manage vast amounts of data for a variety of uses, including high-performance data analytics and the training of machine learning models.
By enabling parallel processing, in which compute servers – known as nodes – work together to boost processing power, HPC allows systems to run advanced, large-scale applications quickly and reliably. Such efficiency adds up to dramatic increases in throughput, which is necessary for processing the exponential amounts of data that come with AI.
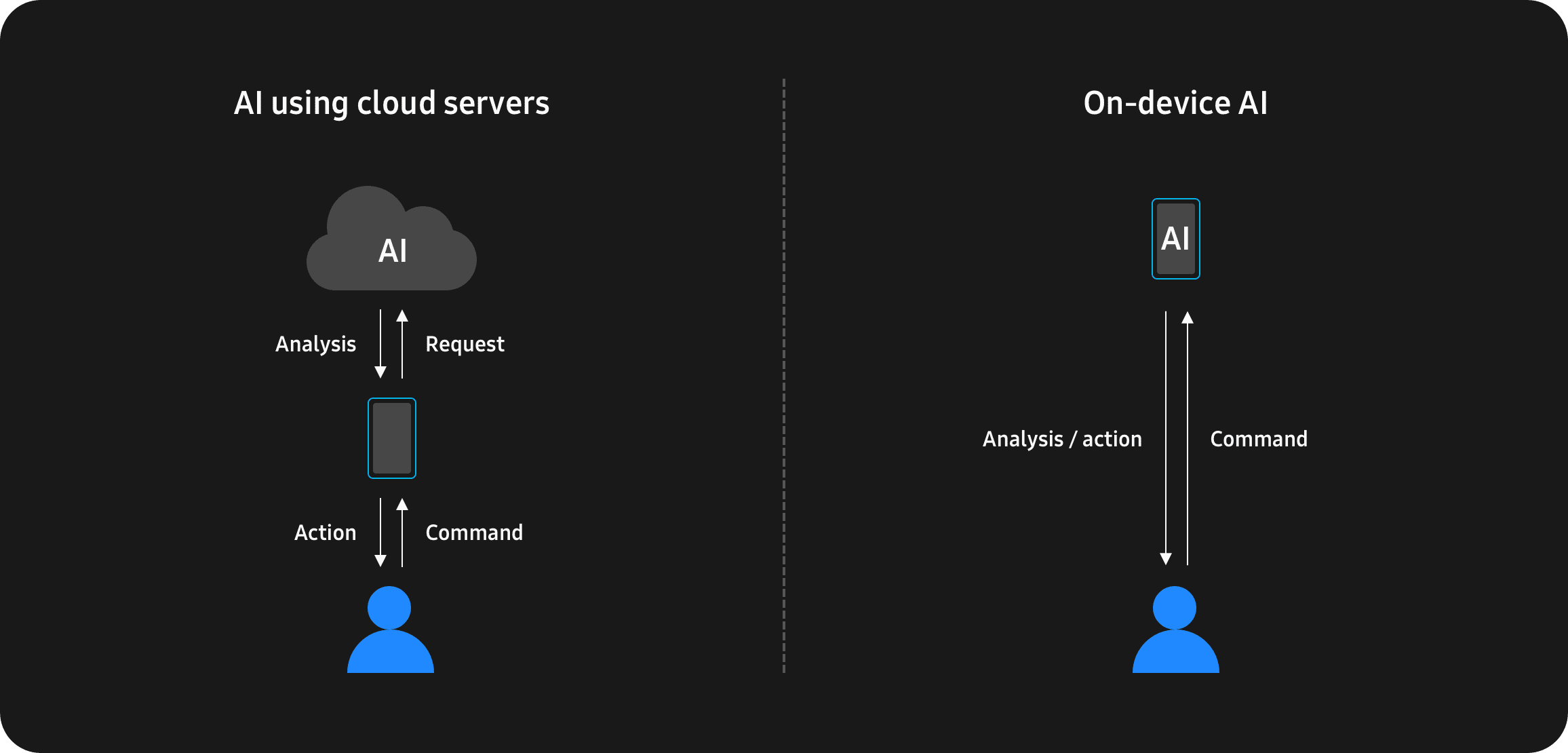
Advancements in on-device AI will play a key part in making connected devices faster and more efficient. Rapid improvements in AI algorithms, hardware and software are making it possible to shift AI services away from the cloud and onto our devices themselves. Localizing these services on mobile devices, appliances, cars and more presents exciting benefits in terms of reliability, privacy and performance.
Not only does on-device AI resolve issues related to network connectivity, it’s also much faster than the cloud because it doesn’t require data to be transmitted to and from a server, and it enables biometric and other sensitive data to be safely confined to the user’s device.
Advancements in on-device AI will play a key part in making connected devices faster and more efficient. Rapid improvements in AI algorithms, hardware and software are making it possible to shift AI services away from the cloud and onto our devices themselves. Localizing these services on mobile devices, appliances, cars and more presents exciting benefits in terms of reliability, privacy and performance.
Not only does on-device AI resolve issues related to network connectivity, it’s also much faster than the cloud because it doesn’t require data to be transmitted to and from a server, and it enables biometric and other sensitive data to be safely confined to the user’s device.
Advancements in on-device AI will play a key part in making connected devices faster and more efficient. Rapid improvements in AI algorithms, hardware and software are making it possible to shift AI services away from the cloud and onto our devices themselves. Localizing these services on mobile devices, appliances, cars and more presents exciting benefits in terms of reliability, privacy and performance.
Not only does on-device AI resolve issues related to network connectivity, it’s also much faster than the cloud because it doesn’t require data to be transmitted to and from a server, and it enables biometric and other sensitive data to be safely confined to the user’s device.
In addition to enabling much faster processing, greater reliability and tighter data security, on-device AI will revolutionize how we utilize our mobile devices.
AI-powered cameras, for example, are already optimizing photos with better image processing, and enhancing biometric security by providing more accurate facial recognition. Virtual and augmented reality experiences, too, will become more immersive and interactive when AI processing is localized to mobile devices. It will also make virtual assistants smarter and more useful by moving vital functions like natural language processing and speech recognition away from the cloud.
In addition to enabling much faster processing, greater reliability and tighter data security, on-device AI will revolutionize how we utilize our mobile devices.
AI-powered cameras, for example, are already optimizing photos with better image processing, and enhancing biometric security by providing more accurate facial recognition. Virtual and augmented reality experiences, too, will become more immersive and interactive when AI processing is localized to mobile devices. It will also make virtual assistants smarter and more useful by moving vital functions like natural language processing and speech recognition away from the cloud.
In addition to enabling much faster processing, greater reliability and tighter data security, on-device AI will revolutionize how we utilize our mobile devices.
AI-powered cameras, for example, are already optimizing photos with better image processing, and enhancing biometric security by providing more accurate facial recognition. Virtual and augmented reality experiences, too, will become more immersive and interactive when AI processing is localized to mobile devices. It will also make virtual assistants smarter and more useful by moving vital functions like natural language processing and speech recognition away from the cloud.

The impending influx of AI services and technologies will unlock new and dynamic applications for high-performance computing (HPC).
Applications like live-streaming services, which require massive amounts of data to be processed in real time, will deliver crisp and clear content thanks to lightning-fast, HPC-powered IT infrastructures. HPC clusters will also benefit from increased efficiency, facilitating speedy data transmission between compute servers and storage.
In addition, the costs associated with supporting HPC will lower as cluster architectures become more efficient at managing resources – lowering businesses’ TCO (total cost of ownership).
The impending influx of AI services and technologies will unlock new and dynamic applications for high-performance computing (HPC).
Applications like live-streaming services, which require massive amounts of data to be processed in real time, will deliver crisp and clear content thanks to lightning-fast, HPC-powered IT infrastructures. HPC clusters will also benefit from increased efficiency, facilitating speedy data transmission between compute servers and storage.
In addition, the costs associated with supporting HPC will lower as cluster architectures become more efficient at managing resources – lowering businesses’ TCO (total cost of ownership).
The impending influx of AI services and technologies will unlock new and dynamic applications for high-performance computing (HPC).
Applications like live-streaming services, which require massive amounts of data to be processed in real time, will deliver crisp and clear content thanks to lightning-fast, HPC-powered IT infrastructures. HPC clusters will also benefit from increased efficiency, facilitating speedy data transmission between compute servers and storage.
In addition, the costs associated with supporting HPC will lower as cluster architectures become more efficient at managing resources – lowering businesses’ TCO (total cost of ownership).
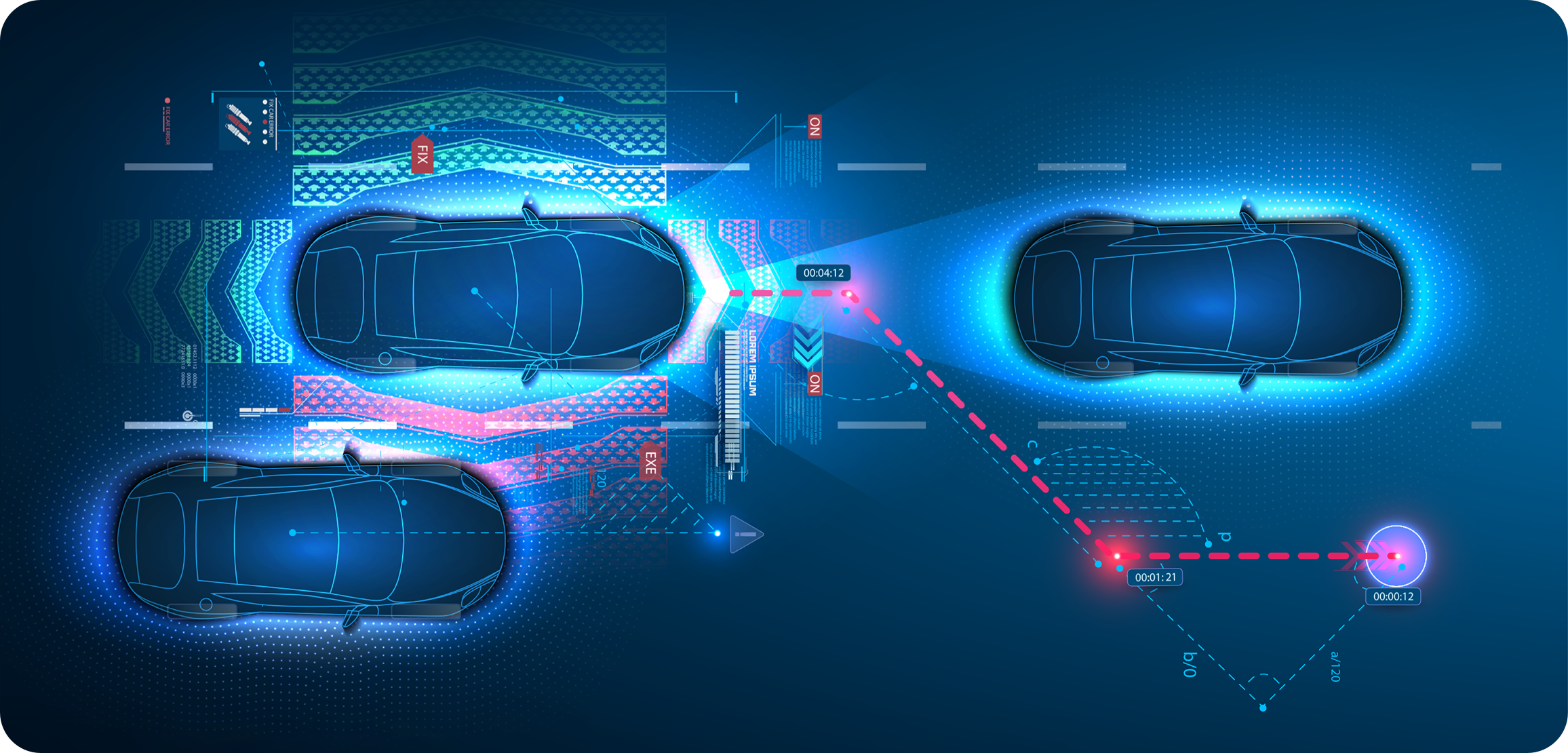
Not only has AI paved the way for the development of self-driving cars, it also holds the keys to making our commutes safer and more efficient.
Connected vehicles employ dozens or even hundreds of sensors to, among other functions,
1) detect potential hazards before drivers see them, and take control of the wheel to avoid accidents,
2) monitor critical components to help prevent failure, and
3) monitor the driver’s gaze and head position to detect when they may be distracted or drowsy. Talk about driving innovation!.
Not only has AI paved the way for the development of self-driving cars, it also holds the keys to making our commutes safer and more efficient.
Connected vehicles employ dozens or even hundreds of sensors to, among other functions,
1) detect potential hazards before drivers see them, and take control of the wheel to avoid accidents,
2) monitor critical components to help prevent failure, and
3) monitor the driver’s gaze and head position to detect when they may be distracted or drowsy. Talk about driving innovation!.
Not only has AI paved the way for the development of self-driving cars, it also holds the keys to making our commutes safer and more efficient.
Connected vehicles employ dozens or even hundreds of sensors to, among other functions,
1) detect potential hazards before drivers see them, and take control of the wheel to avoid accidents,
2) monitor critical components to help prevent failure, and
3) monitor the driver’s gaze and head position to detect when they may be distracted or drowsy. Talk about driving innovation!.

Artificial intelligence is changing the way we enjoy our favorite entertainment by enabling smart TVs to truly live up to their name.
Manufacturers like Samsung are using AI to offer users more personalized content recommendations, and allow them to control their TVs with simple voice commands. In addition, several of Samsung’s latest TVs utilize machine learning to enable users to enjoy their favorite content in the most immersive resolution available: 8K. A built-in AI processor upscales content of all kinds into crystal clear 8K, taking users’ viewing experiences to the next level.
Artificial intelligence is changing the way we enjoy our favorite entertainment by enabling smart TVs to truly live up to their name.
Manufacturers like Samsung are using AI to offer users more personalized content recommendations, and allow them to control their TVs with simple voice commands. In addition, several of Samsung’s latest TVs utilize machine learning to enable users to enjoy their favorite content in the most immersive resolution available: 8K. A built-in AI processor upscales content of all kinds into crystal clear 8K, taking users’ viewing experiences to the next level.
Artificial intelligence is changing the way we enjoy our favorite entertainment by enabling smart TVs to truly live up to their name.
Manufacturers like Samsung are using AI to offer users more personalized content recommendations, and allow them to control their TVs with simple voice commands. In addition, several of Samsung’s latest TVs utilize machine learning to enable users to enjoy their favorite content in the most immersive resolution available: 8K. A built-in AI processor upscales content of all kinds into crystal clear 8K, taking users’ viewing experiences to the next level.

Artificial intelligence, data centers, hyper-connections, and Metaverse are the major platforms that are continuously reshaping our lives in the age of digital transformation.
Looking at the growth of these new platforms, it is clear that their growth goes hand in hand with the advancement of semiconductor technology, just as PCs and smartphones did in the past. As one evolves, so does the other, which triggers new developments and creates the need for the next innovation.
Through a wide range of advanced semiconductor products and technologies, Samsung is laying the foundation for more advanced artificial intelligence in a variety of applications.
In order to implement super-giant AI at the same level as generative AI that the world is enthusiastic about, it is necessary to process an enormous amount of data at high speed. However, a new paradigm of memory technology is absolutely necessary as the existing computing structure has reached its limits.
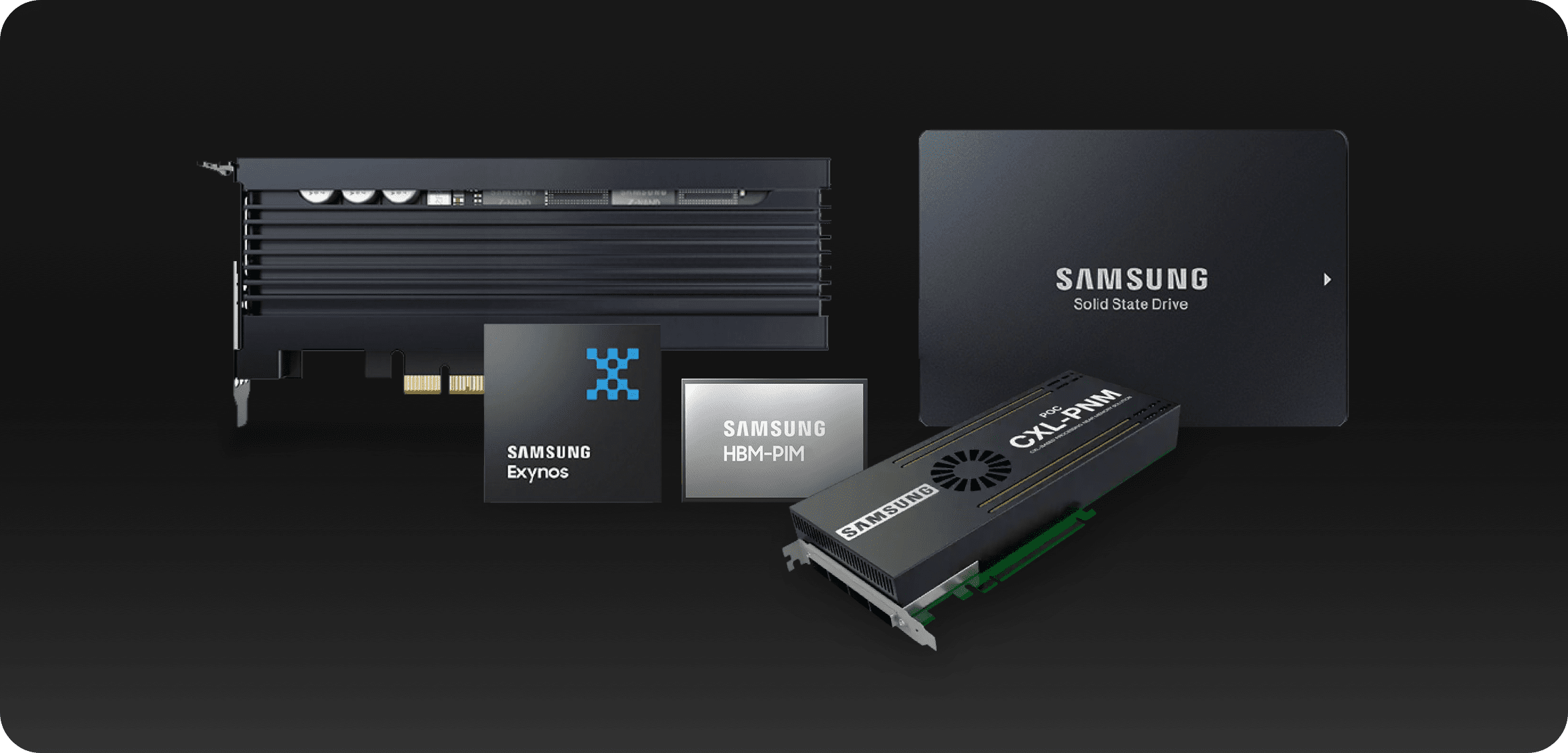
HBM-PIM (Processing-In-Memory) is a product that changes the central processing unit CPU-centered centralized calculation processing process to a decentralized type by designing HBM (High Bandwidth Memory), an ultra-high-speed memory, to take charge of some of the direct computation functions. It is hailed as a next-generation memory technology that can dramatically improve overall data processing by changing the existing architecture in which only the CPU is in charge of computations so that some computations are performed in memory.
In the case of language models used for generative AI, it is estimated that more than 80% of all computation functions may be accelerated by applying PIM. As a result of calculating the performance improvement effects by applying HBM-PIM, it was confirmed that the performance of AI models improved approximately 3.4x more in comparison to using HBM and GPU accelerators.
Like the HBM-PIM mentioned above, CXL-PNM (Processing-Near-Memory) is also a technology incorporating arithmetic functions into memory semiconductors. By placing computation functions next to memory, data movement between the CPU and memory is reduced, thereby reducing bottlenecks and maximizing the processing power of the CPU.
CXL-based PNM solutions can provide 4 times the capacity of existing graphics processing unit (GPU) accelerators by utilizing the CXL interface, which makes it easy to add memory capacity. It is suitable for processing AI models that meet various customer needs at once, and can also be used for super-giant AI language models. Also, compared to an accelerator using a PCIe interface, the AI model loading speed is more than twice as fast.
Samsung Electronics is continuing its efforts to expand the AI memory ecosystem by releasing HBM-PIM and CXL-PNM solutions as well as supporting software, execution methods, and performance evaluation environments as open sources.
The Exynos processor is equipped with an advanced neural network processing unit (NPU) for more powerful and efficient on-device AI, and memory solutions such as LPDDR5 are optimized for high-performance processing required to implement AI systems.
Artificial intelligence, data centers, hyper-connections, and Metaverse are the major platforms that are continuously reshaping our lives in the age of digital transformation.
Looking at the growth of these new platforms, it is clear that their growth goes hand in hand with the advancement of semiconductor technology, just as PCs and smartphones did in the past. As one evolves, so does the other, which triggers new developments and creates the need for the next innovation.
Through a wide range of advanced semiconductor products and technologies, Samsung is laying the foundation for more advanced artificial intelligence in a variety of applications.
In order to implement super-giant AI at the same level as generative AI that the world is enthusiastic about, it is necessary to process an enormous amount of data at high speed. However, a new paradigm of memory technology is absolutely necessary as the existing computing structure has reached its limits.
HBM-PIM (Processing-In-Memory) is a product that changes the central processing unit CPU-centered centralized calculation processing process to a decentralized type by designing HBM (High Bandwidth Memory), an ultra-high-speed memory, to take charge of some of the direct computation functions. It is hailed as a next-generation memory technology that can dramatically improve overall data processing by changing the existing architecture in which only the CPU is in charge of computations so that some computations are performed in memory.
In the case of language models used for generative AI, it is estimated that more than 80% of all computation functions may be accelerated by applying PIM. As a result of calculating the performance improvement effects by applying HBM-PIM, it was confirmed that the performance of AI models improved approximately 3.4x more in comparison to using HBM and GPU accelerators.
Like the HBM-PIM mentioned above, CXL-PNM (Processing-Near-Memory) is also a technology incorporating arithmetic functions into memory semiconductors. By placing computation functions next to memory, data movement between the CPU and memory is reduced, thereby reducing bottlenecks and maximizing the processing power of the CPU.
CXL-based PNM solutions can provide 4 times the capacity of existing graphics processing unit (GPU) accelerators by utilizing the CXL interface, which makes it easy to add memory capacity. It is suitable for processing AI models that meet various customer needs at once, and can also be used for super-giant AI language models. Also, compared to an accelerator using a PCIe interface, the AI model loading speed is more than twice as fast.
Samsung Electronics is continuing its efforts to expand the AI memory ecosystem by releasing HBM-PIM and CXL-PNM solutions as well as supporting software, execution methods, and performance evaluation environments as open sources.
The Exynos processor is equipped with an advanced neural network processing unit (NPU) for more powerful and efficient on-device AI, and memory solutions such as LPDDR5 are optimized for high-performance processing required to implement AI systems.
Artificial intelligence, data centers, hyper-connections, and Metaverse are the major platforms that are continuously reshaping our lives in the age of digital transformation.
Looking at the growth of these new platforms, it is clear that their growth goes hand in hand with the advancement of semiconductor technology, just as PCs and smartphones did in the past. As one evolves, so does the other, which triggers new developments and creates the need for the next innovation.
Through a wide range of advanced semiconductor products and technologies, Samsung is laying the foundation for more advanced artificial intelligence in a variety of applications.
In order to implement super-giant AI at the same level as generative AI that the world is enthusiastic about, it is necessary to process an enormous amount of data at high speed. However, a new paradigm of memory technology is absolutely necessary as the existing computing structure has reached its limits.
HBM-PIM (Processing-In-Memory) is a product that changes the central processing unit CPU-centered centralized calculation processing process to a decentralized type by designing HBM (High Bandwidth Memory), an ultra-high-speed memory, to take charge of some of the direct computation functions. It is hailed as a next-generation memory technology that can dramatically improve overall data processing by changing the existing architecture in which only the CPU is in charge of computations so that some computations are performed in memory.
In the case of language models used for generative AI, it is estimated that more than 80% of all computation functions may be accelerated by applying PIM. As a result of calculating the performance improvement effects by applying HBM-PIM, it was confirmed that the performance of AI models improved approximately 3.4x more in comparison to using HBM and GPU accelerators.
Like the HBM-PIM mentioned above, CXL-PNM (Processing-Near-Memory) is also a technology incorporating arithmetic functions into memory semiconductors. By placing computation functions next to memory, data movement between the CPU and memory is reduced, thereby reducing bottlenecks and maximizing the processing power of the CPU.
CXL-based PNM solutions can provide 4 times the capacity of existing graphics processing unit (GPU) accelerators by utilizing the CXL interface, which makes it easy to add memory capacity. It is suitable for processing AI models that meet various customer needs at once, and can also be used for super-giant AI language models. Also, compared to an accelerator using a PCIe interface, the AI model loading speed is more than twice as fast.
Samsung Electronics is continuing its efforts to expand the AI memory ecosystem by releasing HBM-PIM and CXL-PNM solutions as well as supporting software, execution methods, and performance evaluation environments as open sources.
The Exynos processor is equipped with an advanced neural network processing unit (NPU) for more powerful and efficient on-device AI, and memory solutions such as LPDDR5 are optimized for high-performance processing required to implement AI systems.
Up to three products are comparable at the same time. Click Export button to compare more than three products.
All product specifications reflect internal test results and are subject to variations by the user's system configuration
All product images shown are for illustration purposes only and may not be an exact representation of the product
Samsung reserves the right to change product images and specifications at any time without notice
For further details on product specifications, please contact the sales representative of your region.